Solution: Plant Safety: Bow-Tie
Solution: Plant Safety: Bow-Tie
Bow-Tie Analysis is a structured, qualitative method for risk assessment. The result is a diagram that combines both the chain of cause and hazard (fault tree) as well as the chain of consequence steps (event tree). The fault tree on the left and the event tree on the right are connected by the associated top event (such as a product release) in the middle.
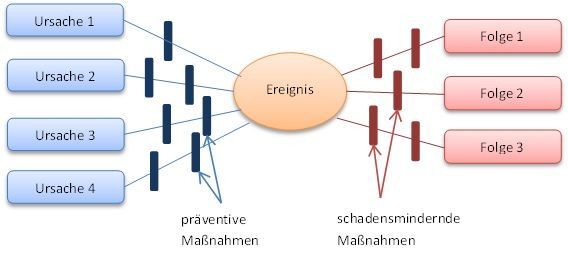
The Bow-Tie diagram provides a snapshot of the cause/hazard and consequences of the main scenarios as well as control elements at the time of analysis. It also provides a snapshot of the barriers used to prevent the occurrence of the adverse event or to limit its impact. Once the examination is complete, the situation may change, for example because control measures have taken effect.
Bow-Tie diagrams are created by depicting following building blocks:
- Hazard (example: presence of hydrocarbons)
- Top event due to hazard (example: product release)
- Causes that enable the occurrence of a top event
- Consequences due to the occurrence of a top event
- Barriers which are intended to prevent the occurrence of the top event on the causal side (preventive control barriers)
- Barriers intended to reduce the extent of damage once a top event has occurred (mitigative barriers)
A Bow-Tie diagram should be prepared, if possible, for all Major Accident Hazards (MAHs) which are to be identified in a hazard and risk analysis if necessary.